
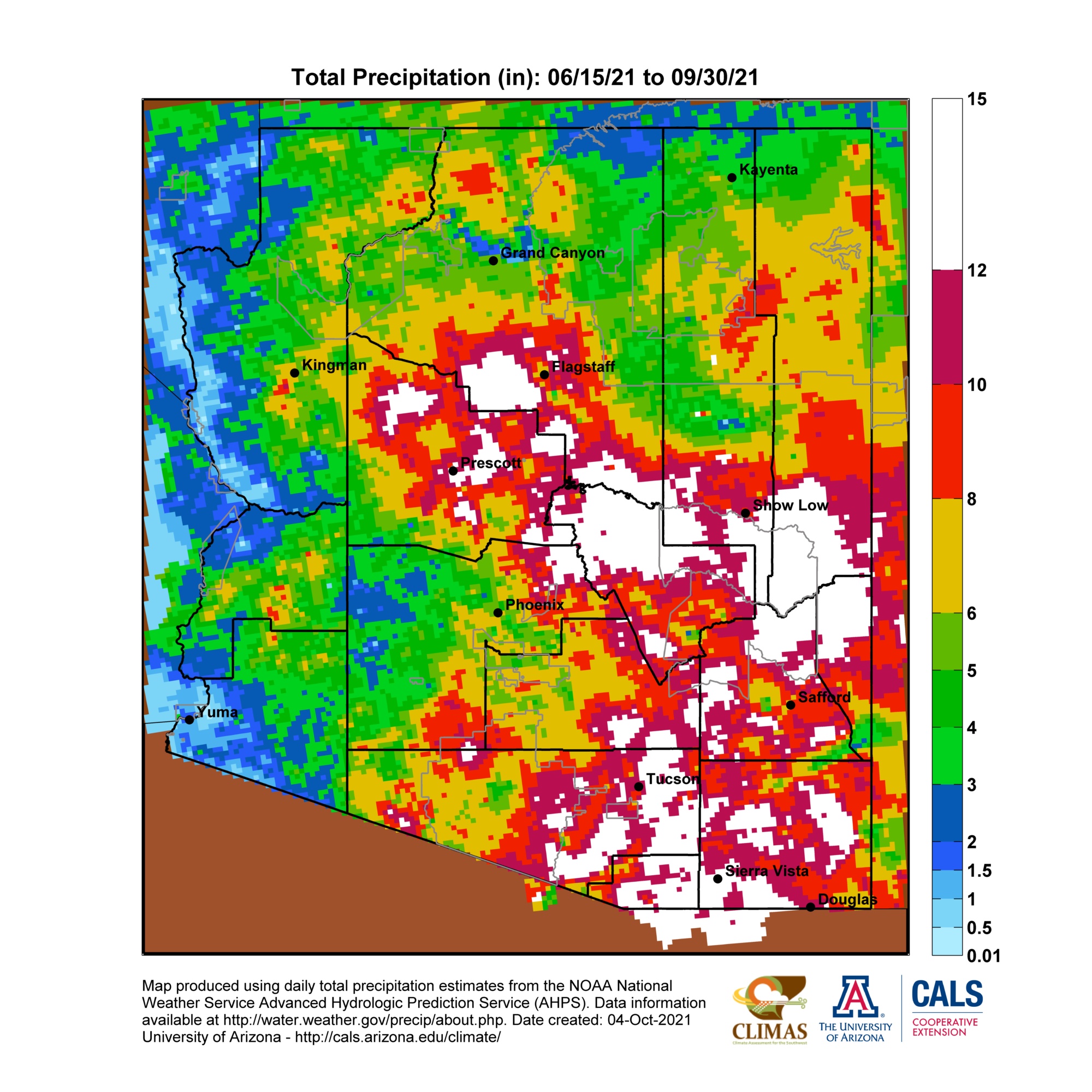
Gague analysis microwave and infrared observations from polar orbiting and geostationary satellitesĬMORPH (CPC MORPHing technique): High resolution precipitation (60S-60N)Ĭlimate Prediction Center/R. Swiss Federal Research Institute WSL,University of Hamburg,University of Zurich,University of GoettingenĮRA-Interim downscaled with geographic predictors and bias-corrected precipĬHOMPS: CICS High-Resolution Optimally Interpolated Microwave Precipitation from SatellitesĬMAP: CPC Merged Analysis of Precipitation Over oceans only,Behrangi et al (2014), 'estimate for 3-yr (2007–09) near-global (80S-80N) oceanic mean precipitation rate is ~2.94 mm/day which is about 9% than the CPC/CMAP rate (2.68 mm/day) and 4% higher than the GPCP rate (2.82 mm/day)'.ĪPHRODITE: Asian Precipitation - Highly-Resolved Observational Data Integration Towards Evaluation of Water ResourcesĠ.25x0.25, 0.5x0.5 (whole Asia), 0.05x0.05 (Japan only)ĬHELSA high-resolution land surface temperature and precipitation Adler et al (2012) estimate the global (ocean+land)-mean precipitation as 2.6 ± 7% mm/day.

Moreover, wind and evaporation effects on the gauge measurments, typically resulting in under-catch, need to be considered.ĭespite many advances in observing systems and algorithms over the years, validating global precipitation observations, for example through the energy budget approach, has proven challenging. Microwave-only products include CHOMPS and the SSM/I datasets PERSIANN and CMORPH combine information from passive microwave and infrared.Ĭlimate-quality, gauge-based data sets can be difficult to construct due to the widely distributed and heterogeneous nature of the source data. The microwave-based algorithms derive the precipitation signal from both scattering and emission but only the scattering signal is useful over land because of strong variations in surface emissivity that distort the emission. Infrared sensors are used to estimate cloud top temperatures, which must be calibrated to some other precipitation estimate. For this reason, many data sets combine observations from multiple satellite platforms that carry passive microwave and/or infrared instruments. GPCP, CMAP, TRMM 3B42).Įven with the near-global coverage of satellites, most satellites fly over a region only twice per day, potentially missing precipitation events. CRU TS, GPCC, APHRODITE, PREC/L), satellite-only data sets (e.g., CHOMPS) and merged satellite-gauge products (e.g. Most precipitation data sets may be categorized into one of three broad categories: gauge data sets (e.g. Further, regional variations in topography can affect precipitation amounts significantly. Unlike (say) temperature which has a high degree of spatial and temporal correlation, precipitation can be fractal in space and discontinuous in time. However, the very nature of precipitation and the limitations of the observing system make the quantification of precipitation challenging. Hence, high quality estimates of precipitation's distribution, amounts and intensity are essential. For climate research, precipitation is one of the key terms for balancing the energy budget, and one of the most challenging aspects of climate modeling. Its societal importance cannot be over stated. ) is one of the key components of the hydrological cycle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
